You’d be horrified by how much we can find about you online.
We often implicitly trust companies to keep our data safe, but wait a minute – just because they say it’s safe doesn’t mean it’s foolproof. In fact, companies often warn you in their contracts about how they will handle your information.
That’s not possible, you might say. Well, just recently, in July 2024, AT&T confirmed that cybercriminals had stolen phone numbers and call records of “nearly all” of its customers, affecting approximately 110 million people [1].
The genetic testing company ’23andMe’ reported a breach, affecting 14,000 users [2].
Under the subtitle “Top 5 Data Breaches of 2023,” you can read about this genetic company and others [2].
Here’s an altered story – almost real (company names and personal names have been changed to guarantee anonymity) – that will make you think twice about your own online security… and even your physical security:
The High-School Friend and The DNA Test
Juliana Luniq, a young German medical professional, had just moved to a new city, Amsterdam. She was juggling her new job while setting up her new place, keeping her busy and somewhat feeling lonely. A few days after settling in, she was thrilled to reconnect with Amanda, her best friend from high school. Amanda had reached out on social media, and soon they were remembering about old times, laughing over high-school photos, and catching up on Juliana’s new life that Amanda had followed on social media, where Juliana posted her move from Germany to the Netherlands.
Juliana felt a wave of nostalgia as she reconnected with Amanda, who remembered all the details – favorite bands, embarrassing prom moments, even the long summer road trip they had taken after graduation.
It was comforting to have an old friend in her inbox, especially while adjusting to a new city and all the challenges of starting fresh. Juliana and Amanda chatted over the next few weeks, catching up on everything from career to family. Juliana even shared that she had recently taken a DNA test with a popular international company, GeneVII GmbH, to explore her ancestry and potential health risks. She had always been interested in her heritage, and the test had provided insights into her family’s genetic makeup, along with a few notes on health predispositions.
Unknown to Juliana, the “Amanda” she thought she was chatting with was not her friend at all. The real Amanda had no idea this “reconnection” was happening. Juliana was, in fact, being targeted by a sophisticated scam ring that exploited leaked data from GeneVII GmbH and social media. By piecing together both Amanda’s and Juliana’s social media posts, tagged photos (dates, places…), and even Juliana’s genetic data, the scam ring crafted a disturbingly convincing persona from Juliana’s past. Like so many of us – even high-profile cybersecurity experts who’ve been targeted – Juliana had unknowingly provided the foundation they needed.
Over the next few weeks, “Amanda” became a comforting presence for Juliana – a familiar face who seemed to understand her. They exchanged stories and recommendations, and one day, “Amanda” suggested an exclusive supplemental health analysis service from GeneVII GmbH that she had found after Juliana had recommended the company to her. The offer seemed like the perfect opportunity for Juliana to explore her health profile in greater depth, especially with the recommendation from her friend.
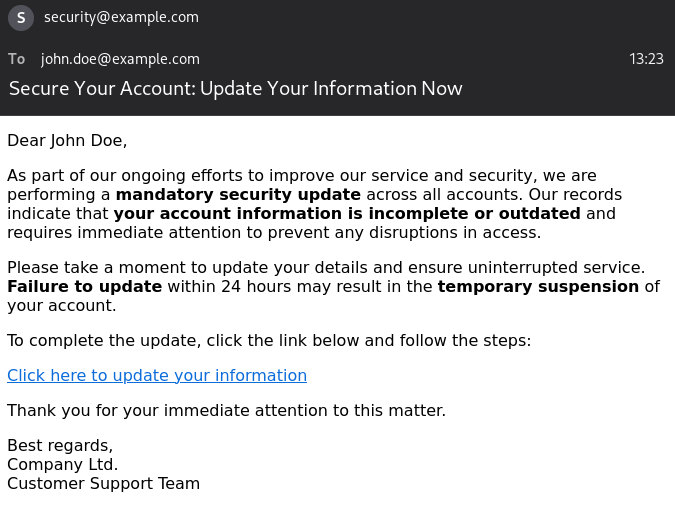
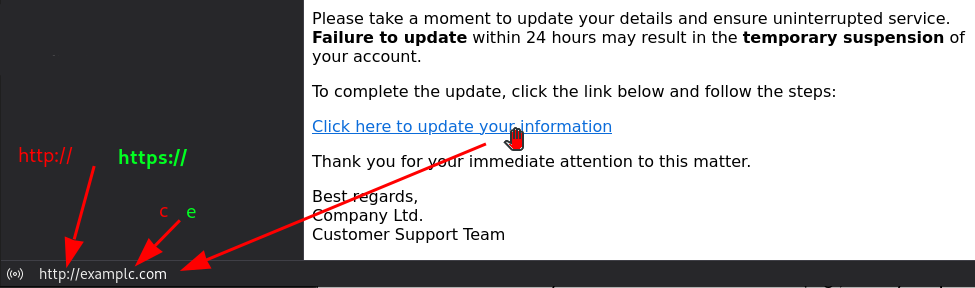
Juliana clicked the fake link sent to her, logged in, provided her details, and verified her account “for security purposes” via a 6-digit Google Authenticator code (any code would work), thinking this was just another benefit of her GeneVII GmbH membership. The address had only a slight change – where ‘VII’ had one lowercase ‘L’ instead of two (unnoticeable).
That very night, the scam operation went into action. “Amanda” and her team now had complete access to Juliana’s GeneVII GmbH account, including her full genetic profile. Worse still, they had changed her security questions, password, and locked her out – a move timed over the weekend when most companies are closed. As a precaution, they also accessed her email, confirmed all changes, and deleted any email notifications.
On Monday, while Juliana was at work, her family received an unexpected call from a professional-sounding woman claiming to be a genetic counselor from GeneVII GmbH. She explained that, through routine analysis, they had discovered a serious genetic marker for an aggressive disease in Juliana’s DNA. The counselor’s tone was calm, compassionate, and and eerily calm. She warned Juliana’s parents that their daughter was at imminent risk for the disease and that a groundbreaking, though experimental, treatment was available privately.
“We’re reaching out because Juliana didn’t respond to her emergency contact,” the counselor said smoothly, spinning a believable story that left Juliana’s parents in a state of panic. Her father tried to contact her directly, but each attempt was met with an error message asking him to try again later. The scammers had managed to block her account and used a pretense with the operator to change her phone number.
In the midst of this supposed crisis, the counselor put the family in touch with “Amanda”, claiming that Juliana had trusted her as a local contact in Amsterdam. Tearfully, “Amanda” explained that Juliana had confided in her about feeling fatigued and overwhelmed, and was considering this experimental treatment – if only it weren’t so costly. To make the story even more convincing, “Amanda” shared personal, intimate details about her supposed friend.
Juliana’s family was devastated. Unable to reach her, feeling powerless and desperate, they resolved to do anything to save her. The counselor assured them that EUR 80,000 was all that was needed to secure a spot in the exclusive medical trial, but emphasized that spots were filling up quickly.
In an emotional rush, Juliana’s parents wired the money, convinced they were buying their daughter precious time. All the while, Juliana was blissfully unaware of the deception, still going about her happy life in Amsterdam.
That evening, she only discovered the truth when she tried to log into her GeneVII GmbH account to do what “Amanda” told her about the new test and found she was locked out. Panicked, she called the company’s customer service, only to learn that her account had been accessed from a new device two days earlier, and her details had been changed. Her heart raced as she thought, ‘Who could that be?’ when suddenly all the private messages she had exchanged with “Amanda” came to mind, making her realize that her supposed friend had known far too much. It struck her like a ton of bricks that this “friend” was a complete stranger, piecing together her life and vulnerabilities through years of social media, and now genetic data.
With mounting dread, she urgently called her parents from the company’s phone since her own phone was disabled – only to learn of the money they had sent and the horror they had endured on her behalf. They were all heartbroken, and Juliana was devastated at having unknowingly led them there. Every choice she had made seemed to unravel with one simple, careless mistake:
Trusting an ‘online friend request’ from someone who felt familiar.
Juliana had fallen victim to a deeply personal scam, one that exploited intimate details of her life, her genetic data, and her family’s trust. A single click, a connection with a “familiar” face, and a series of misplaced trust had led her and her family into the hands of a highly organized scam ring.
What can we take away from this story?
Every digital footprint you leave online remains permanent – whether you ask Google to remove it or not. Think beyond just Google, and consider other search engines outside the EU and US, and especially governmental databases. Your photos, friendships, and even your DNA can be weaponized by bad actors. In an age where data breaches occur daily and scammers exploit the smallest details, it’s crucial to rethink who you trust online and what data you share. Your information might be worth more than you realize – not just to you, but to those who would use it against you and the people you love.
This story serves as a reminder to think carefully about the personal information you share, even with online friends (check with them before, via email, telephone…), to recognize the potential for deep personal consequences. Be proactive by asking questions!
In our days, we urgently need to exercise caution when it comes to our data in today’s digital world. Be mindful of what you share on social media, and consider removing tags and geolocation data from your photos and videos.
Just for fun (or maybe not), try asking ChatGPT to create a profile about you – you will be amazed at what it can tell you. Now just imagine governments who collect every bit of data about you, and using a more powerful AI!
A new DANGER!
A new threat is now looming, the imitation of our voices, which could be used to scam us all.
These AI-generated voices can be incredibly realistic, to the point that it becomes difficult to tell if you are speaking to a human or a machine. Imagine receiving a call from a loved one, asking for money urgently, only to find out it was not them at all, but a deepfake of their voice.
Advise your friends or loved ones to take action if they notice anything unusual or suspicious. For instance, they can use security-based questions to verify whether they are truly speaking to the person they think they are. These questions could be designed to test familiarity or mutual knowledge that only the real person would know. Here are some examples:
- “What was the color of my childhood bedroom?” (A personal question based on shared history.)
- “What’s the name of the family dog?” (A detail that’s specific and difficult for an imposter to guess.)
- “What was the title of the last movie we watched together?” (Something that could easily reveal whether the caller is the real person or not.)
- “Can you name the musical band we saw last summer?” (A shared experience that would be hard for anyone else to know.)
- “What was the first thing I said when we met?” (A personal memory that only the real person would be able to recall.)
- …
These questions can help confirm that the person on the other end is who they claim to be, especially in cases where AI-generated voices might be used to deceive. In fact, you could even use these questions while chatting, as AI currently excels more in text-based conversations than in voice interactions.
Be proactive in educating your circle about these potential threats, and always verify anything that seems even slightly out of the ordinary.
Is the first sentence justified?
“You’d be horrified by how much we can find about you online.”
Disclaimer:
The names, places, companies, and, in part, events mentioned in this article are purely fictional and created solely for illustrative purposes. Any resemblance to actual individuals, locations, or organizations is entirely coincidental.
References:
[1] https://techcrunch.com/2024/10/14/2024-in-data-breaches-1-billion-stolen-records-and-rising/
[2] https://jumpcloud.com/blog/top-data-breaches-2023